L-Galaxies Workshop (10-12, Feb., 2016): during the workshop we will release the Henriques2015a version of the L-Galaxies code and give tutorials on how to run and modify it and to use the MCMC sampler.
Semi-analytic models of galaxy formation are built on a description of the redshift evolution of the mass and number density of dark matter halos in terms of their merger history (the so-called merger trees). The evolution of the baryonic component hosted by these halos is then followed by means of a set of parametrised, physically based equations, to describe the physical processes that affect galaxy formation and evolution. The Munich galaxy formation model includes physical prescriptions for processes such as gas cooling, star formation, supernova feedback, formation and growth of black holes, AGN feedback and galaxy interactions and mergers that have been gradually developed over the years. A few simple slides describing the main components of the model can be found in LGalaxies_slides.pdf .
The recent Henriques2015a release scales the Millennium and Millennium-II simulations to the cosmology of the first year PLANCK data. MCMC methods were used to explore the full high-dimensional parameter space of the galaxy formation model in order to identify regions which could reproduce the observed abundances and quenched fractions of galaxies as a function of stellar mass from z=3 down to z=0. Matching these more extensive and more precise observational results required a delayed reincorporation of wind ejecta, a lower surface density threshold for turning cold gas into stars, the elimination of ram-pressure stripping in haloes less massive than \(∼10^{14} M_{\odot}\), and a modification to the radio mode feedback model. These changes cure the most obvious failings of previous versions of the model, namely the overly early formation of low-mass galaxies and the overly large fraction of them that are passive at late times. 4 million CPU hours were used, and over 20 million representations of the Universe were evaluated, in order to build this model.
Catalogues released for this model include snapshots of the (sub)halo and galaxy populations with extended photometric coverage and star formation and metallicity histories, as well as lightcones with photometry based on two different stellar population synthesis models. These are available in the Millennium Database.
Full description of the current model release: L-Galaxies_Documentation.pdf
MNRAS article: Henriques et al., 2015, MNRAS, 451, 2663
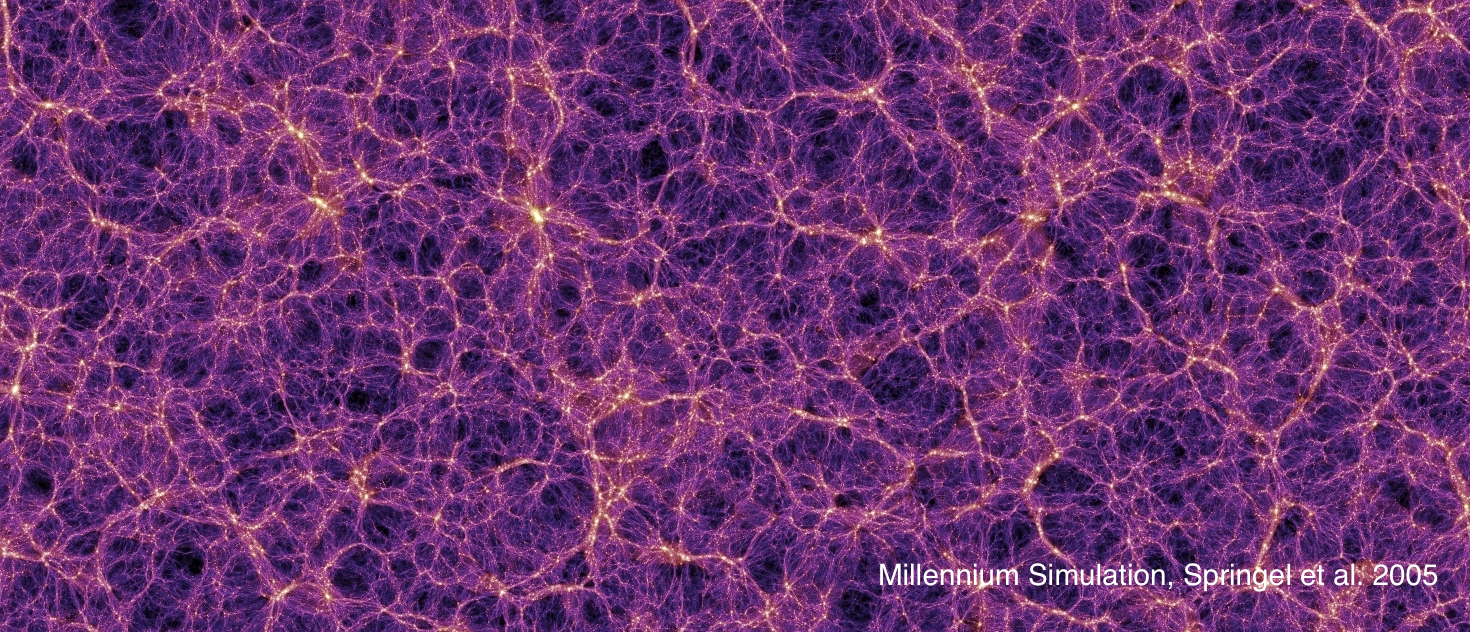
A snapshot of the dark matter only simulation:

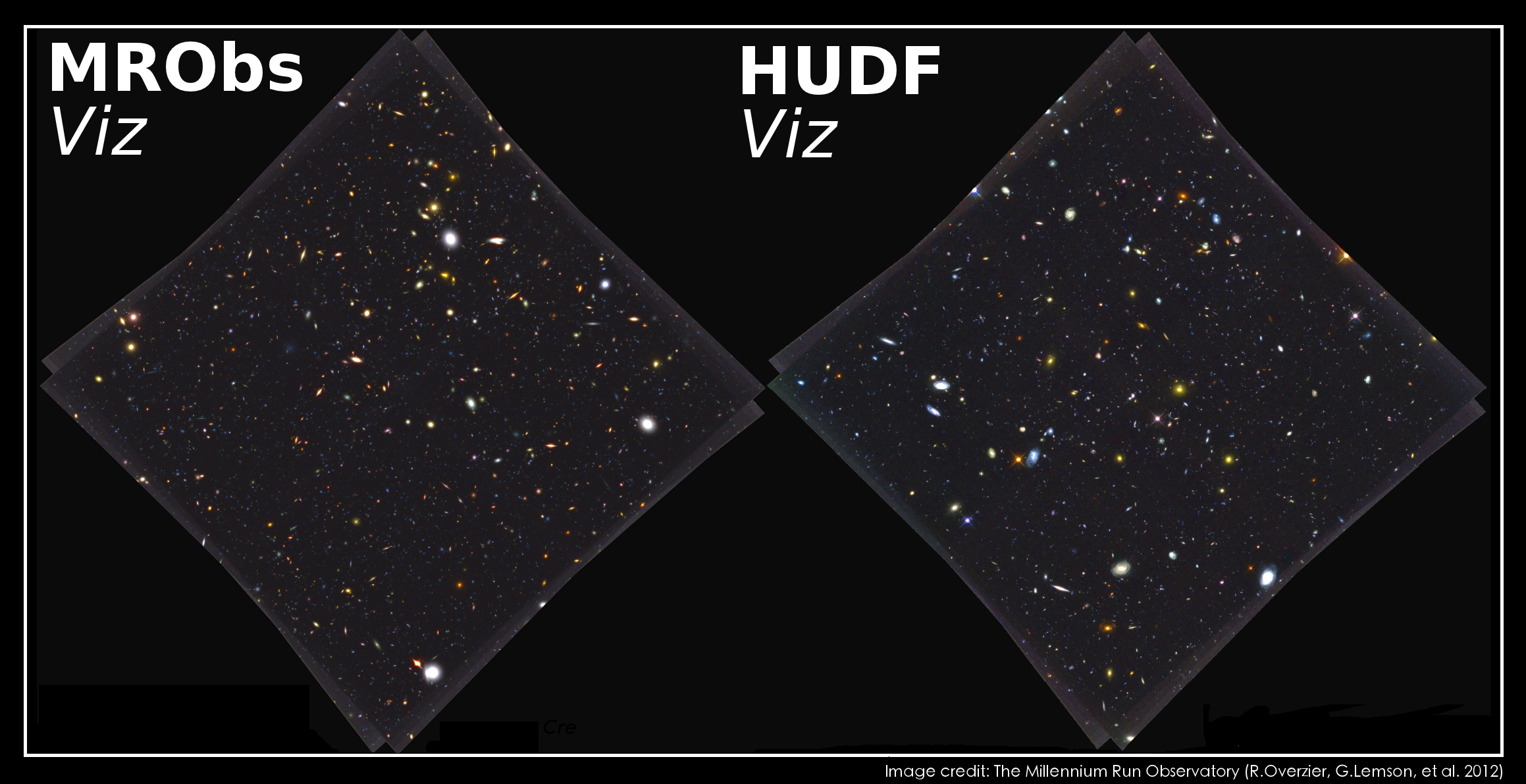
On the left, simulated galaxies seen through a lightcone, on the right, real data from HST: